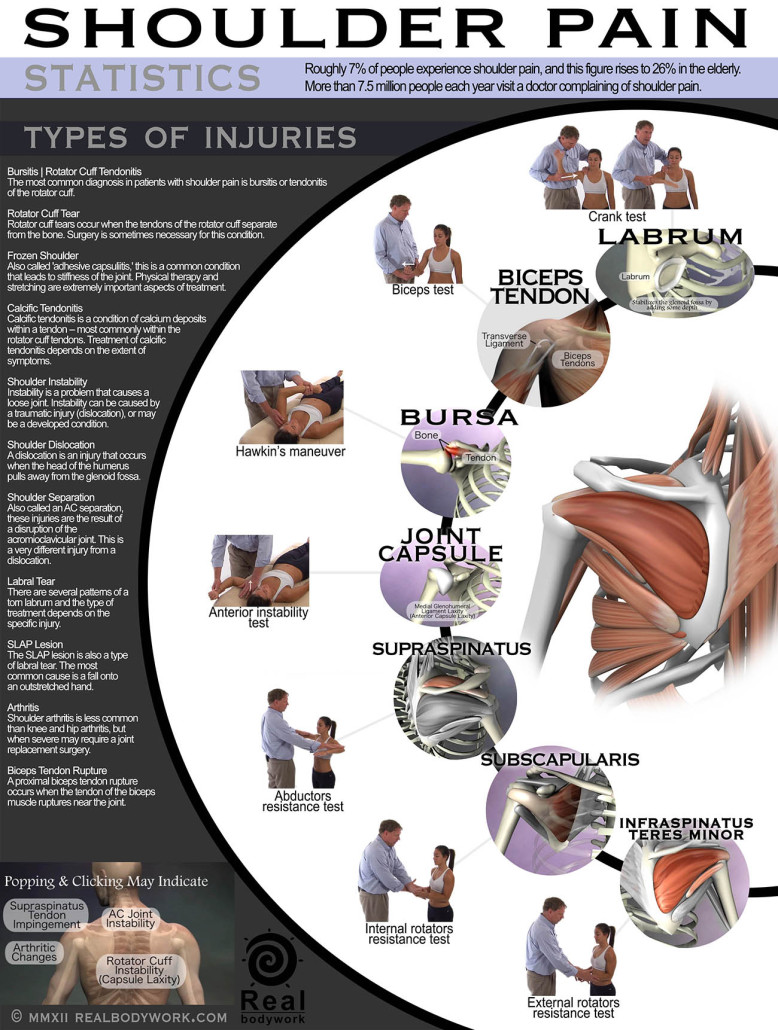
Once this collection of substances enters the lymphatic vessels it is known as lymph; lymph is subsequently filtered by lymph nodes and directed into the venous system. This article will explore the anatomy of lymphatic drainage throughout the lower limb, and how this is relevant clinically. Lymph Chains & Their Drainage Areas Lymph Nodes of the Head and Neck. Lymph Nodes at Surface; Deep Lymph Nodes; Lymph Nodes of Breast and Arm. Lymph Nodes of the Breast and Upper Limb; Thoracic Lymph Nodes. Parietal Lymph Nodes of the Thorax; Visceral Lymph Nodes of the Thorax; Lymph Nodes of the Lower Thorax; Abdominal Lymph Nodes. In the early 1950s, Walker was the first to use radiotracers to map lymphatic drainage 5. Following this, Sherman et al. Developed the concept of lymphoscintigraphy 6, demonstrating that colloidal gold could be traced from the point of intradermal injection to the draining lymph nodes. This was the advent of cutaneous lymphoscintigraphy as. Lymphatic drainage map Lymphatic drainage poster that shows the drainage patterns and lymph nodes.
Thoracic lymph nodes are divided into 14 stations as defined by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 1, principally in the context of oncologic staging. For the purpose of prognostication, the stations may be grouped into seven zones. The IASLC definitions leave some ambiguous regions which can lead to misclassification 3.
Supraclavicular zone
Station 1 (left/right): low cervical, supraclavicular, and sternal notch nodes
- superior border: lower margin of the cricoid cartilage
- inferior border: strictly the IASLC defines this as the clavicles, which leads to ambiguity, particularly as the clavicle is mobile - a more definitive anatomical boundary is the thoracic inlet, i.e. 1st rib2
- left (1L) and right (1R) are divided by the midline of the trachea
- station 1 nodes are outsidethe mediastinum and staged as an N3 disease; despite this, they can sometimes be treated with radical intent if they are encompassable in a radiotherapy field
Upper zone (superior mediastinal nodes)
Station 2 (left/right): upper paratracheal nodes
- superior border: apex of lung / pleural space, thoracic inlet 2
- left (2L) and right (2R) are divided along the left lateral border of the trachea, not the midline
- inferior border of 2R: at the intersection of caudal margin of the left brachiocephalic vein with the trachea, i.e. abuts 4R
- inferior border of 2L: superior border of the aortic arch, i.e. abuts 4L
Station 3A and 3P: pre-vascular and retrotracheal nodes
- superior border: thoracic inlet
- inferior border: carina
- 3A: prevascular - anterior to the great vessels (superior vena cava on the right, left common carotid artery on the left), posterior to the sternum
- 3P: retrotracheal - posterior to the trachea
Station 4 (left/right): lower paratracheal nodes
- left (4L) and right (4R) are divided along the left lateral border of the trachea,not the midline
- 4R:
- superior border: intersection of caudal margin of the left brachiocephalic vein with the trachea, i.e. abuts 2R
- inferior border: inferior border of the azygos vein
- 4L:
- superior border: superior border of the aortic arch, i.e. abuts 2L
- inferior border: superior border of the left main pulmonary artery
- pre-carinal nodes
- lymph nodes anterior to the tracheal bifurcation are inferior to the above anatomic definitions and are thus technically unclassified by IASLC
- these nodes are in the mediastinum (N2) and their surgical management mirrors that of 4R/4L lymph nodes, hence, pre-carinal nodes are best classified as part of the 4R/4L stations 2
Aortopulmonary zone
Station 5: subaortic nodes (aortopulmonary window)
- lateral to ligamentum arteriosum
- superior border: inferior border of the aortic arch
- inferior border: superior border of the left main pulmonary artery
Station 6: para-aortic nodes, ascending aorta or phrenic
- anterior and lateral to the ascending aorta and aortic arch
- superior border: line tangential to the upper border of the aortic arch
- inferior border: lower border of the aortic arch
Subcarinal zone

Station 7: subcarinal nodes
- superior border: carina
- inferior border - left:upperborder of the lower lobe bronchus
- inferior border - right: lowerborder of bronchus intermedius

Lower zone (inferior mediastinal nodes)
Station 8 (left/right): para-esophageal nodes (below carina)
- superior border: station 7, i.e. upper border of lower lobe bronchus on left, and lower border of bronchus intermedius on right
- inferior border: diaphragm
Station 9 (left/right): pulmonary ligament nodes
- lying within the pulmonary ligament
- superior border: inferior pulmonary vein
- inferior border: diaphragm
Hilar and interlobar zone (pulmonary nodes)
Station 10 (left/right): hilar nodes
- immediately adjacent to mainstem bronchus and hilar vessels
- superior border: lower border of the azygos vein on the right, the upper border of the pulmonary artery on the left
Station 11: interlobar nodes
- between the origin of the lobar bronchi
Peripheral zone (pulmonary nodes)
Station 12: lobar nodes
- adjacent to lobar bronchi
Station 13: segmental nodes
- adjacent to segmental bronchi
Station 14: subsegmental nodes
- adjacent to subsegmental bronchi
- subsegmental
- 1. Rusch VW, Asamura H, Watanabe H et-al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: a proposal for a new international lymph node map in the forthcoming seventh edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4 (5): 568-77. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a0d82e - Pubmed citation
- 2. El-Sherief AH, Lau CT, Wu CC, Drake RL, Abbott GF, Rice TW. International association for the study of lung cancer (IASLC) lymph node map: radiologic review with CT illustration. (2014) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 34 (6): 1680-91. doi:10.1148/rg.346130097 - Pubmed
- 3. El-Sherief AH, Lau CT, Obuchowski NA, Mehta AC, Rice TW, Blackstone EH. Cross-Disciplinary Analysis of Lymph Node Classification in Lung Cancer on CT Scanning. (2017) Chest. 151 (4): 776-785. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2016.09.016 - Pubmed
Related Radiopaedia articles
Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton
- thoracic cage
- ribs
- atypical ribs
- variant anatomy
- sternum
- manubrium
- sternal body
- xiphisternum
- ribs
- articulations
- thoracic cage
- muscles of the thorax
- diaphragm
- diaphragmatic apertures
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- diaphragm
- spaces of the thorax
- superior thoracic aperture
- mediastinum
- thoracic plane (mnemonic)
- inferior mediastinum
- thoracic viscera
- tracheobronchial tree
- trachea
- left main bronchus
- right main bronchus
- bronchus intermedius
- tracheobronchial branching anomalies
- trachea
- lungs
- bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy (Boyden Classification) (mnemonic)
- left lung
- left upper lobe
- lingula
- left lower lobe
- left upper lobe
- right lung
- right upper lobe
- right middle lobe
- right lower lobe
- variant anatomy
- left lung
- lung parenchyma
- pulmonary interstitium
- peribronchovascular interstitium
- interlobular septum
- peribronchovascular interstitium
- bronchiole
- terminal bronchiole
- respiratory bronchiole
- terminal bronchiole
- secondary pulmonary lobule
- pulmonary acinus
- primary pulmonary lobule
- alveoli
- primary pulmonary lobule
- pulmonary acinus
- pulmonary interstitium
- hilum
- pleura
- pleural space
- fissures
- accessory fissures
- fissures
- pleural space
- bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy (Boyden Classification) (mnemonic)
- heart
- cardiac chambers
- left atrium
- left atrial appendage
- left ventricle
- right atrium
- right ventricle
- left atrium
- heart valves
- mitral valve
- aortic valve
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- coronary arteries
- left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
- circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
- right coronary artery (RCA)
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- fetal circulation
- atrial septum
- pericardium
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- superior aortic recess
- pulmonic recesses
- pulmonary venous recesses
- aortic recesses
- pericardial space
- cardiac chambers
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- axillary tail
- Montgomery glands
- Cooper ligaments
- lymphatic drainage
- variants
- supranumerary nipple (polythelia)
- accessory breast tissue (polymastia)
- tracheobronchial tree
- blood supply of the thorax
- arteries
- thoracic aorta (development)
- ascending aorta
- aortic root
- aortic arch
- subclavian artery
- internal thoracic artery
- thyrocervical trunk
- transverse cervical artery
- costocervical trunk
- variant anatomy
- branching patterns
- subclavian artery
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
- ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
- left pulmonary artery
- thoracic aorta (development)
- veins
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- variant anatomy
- brachiocephalic veins (retro-aortic)
- azygos vein (azygos system)
- variant anatomy
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
- coronary veins
- cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
- cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- arteries
- lymphatics
- thoracic lymph node stations
- innervation of the thorax
- vagus nerve
Promoted articles (advertising)
Thoracic lymph nodes are divided into 14 stations as defined by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 1, principally in the context of oncologic staging. For the purpose of prognostication, the stations may be grouped into seven zones. Grammarly on onenote online. The IASLC definitions leave some ambiguous regions which can lead to misclassification 3.
Supraclavicular zone
Station 1 (left/right): low cervical, supraclavicular, and sternal notch nodes
- superior border: lower margin of the cricoid cartilage
- inferior border: strictly the IASLC defines this as the clavicles, which leads to ambiguity, particularly as the clavicle is mobile - a more definitive anatomical boundary is the thoracic inlet, i.e. 1st rib2
- left (1L) and right (1R) are divided by the midline of the trachea
- station 1 nodes are outsidethe mediastinum and staged as an N3 disease; despite this, they can sometimes be treated with radical intent if they are encompassable in a radiotherapy field
Upper zone (superior mediastinal nodes)
Station 2 (left/right): upper paratracheal nodes
- superior border: apex of lung / pleural space, thoracic inlet 2
- left (2L) and right (2R) are divided along the left lateral border of the trachea, not the midline
- inferior border of 2R: at the intersection of caudal margin of the left brachiocephalic vein with the trachea, i.e. abuts 4R
- inferior border of 2L: superior border of the aortic arch, i.e. abuts 4L
Station 3A and 3P: pre-vascular and retrotracheal nodes
- superior border: thoracic inlet
- inferior border: carina
- 3A: prevascular - anterior to the great vessels (superior vena cava on the right, left common carotid artery on the left), posterior to the sternum
- 3P: retrotracheal - posterior to the trachea
Station 4 (left/right): lower paratracheal nodes
- left (4L) and right (4R) are divided along the left lateral border of the trachea,not the midline
- 4R:
- superior border: intersection of caudal margin of the left brachiocephalic vein with the trachea, i.e. abuts 2R
- inferior border: inferior border of the azygos vein
- 4L:
- superior border: superior border of the aortic arch, i.e. abuts 2L
- inferior border: superior border of the left main pulmonary artery
- pre-carinal nodes
- lymph nodes anterior to the tracheal bifurcation are inferior to the above anatomic definitions and are thus technically unclassified by IASLC
- these nodes are in the mediastinum (N2) and their surgical management mirrors that of 4R/4L lymph nodes, hence, pre-carinal nodes are best classified as part of the 4R/4L stations 2
Aortopulmonary zone
Station 5: subaortic nodes (aortopulmonary window)
- lateral to ligamentum arteriosum
- superior border: inferior border of the aortic arch
- inferior border: superior border of the left main pulmonary artery
Station 6: para-aortic nodes, ascending aorta or phrenic
- anterior and lateral to the ascending aorta and aortic arch
- superior border: line tangential to the upper border of the aortic arch
- inferior border: lower border of the aortic arch
Subcarinal zone
Station 7: subcarinal nodes
- superior border: carina
- inferior border - left:upperborder of the lower lobe bronchus
- inferior border - right: lowerborder of bronchus intermedius
Lower zone (inferior mediastinal nodes)
Station 8 (left/right): para-esophageal nodes (below carina)
- superior border: station 7, i.e. upper border of lower lobe bronchus on left, and lower border of bronchus intermedius on right
- inferior border: diaphragm
Station 9 (left/right): pulmonary ligament nodes
- lying within the pulmonary ligament
- superior border: inferior pulmonary vein
- inferior border: diaphragm
Hilar and interlobar zone (pulmonary nodes)
Station 10 (left/right): hilar nodes
- immediately adjacent to mainstem bronchus and hilar vessels
- superior border: lower border of the azygos vein on the right, the upper border of the pulmonary artery on the left
Lymph Drainage Map Lymph Flow
Station 11: interlobar nodes
- between the origin of the lobar bronchi
Peripheral zone (pulmonary nodes)
Station 12: lobar nodes
- adjacent to lobar bronchi
Station 13: segmental nodes
- adjacent to segmental bronchi
Station 14: subsegmental nodes
- adjacent to subsegmental bronchi
- subsegmental
- 1. Rusch VW, Asamura H, Watanabe H et-al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: a proposal for a new international lymph node map in the forthcoming seventh edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4 (5): 568-77. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a0d82e - Pubmed citation
- 2. El-Sherief AH, Lau CT, Wu CC, Drake RL, Abbott GF, Rice TW. International association for the study of lung cancer (IASLC) lymph node map: radiologic review with CT illustration. (2014) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 34 (6): 1680-91. doi:10.1148/rg.346130097 - Pubmed
- 3. El-Sherief AH, Lau CT, Obuchowski NA, Mehta AC, Rice TW, Blackstone EH. Cross-Disciplinary Analysis of Lymph Node Classification in Lung Cancer on CT Scanning. (2017) Chest. 151 (4): 776-785. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2016.09.016 - Pubmed
Related Radiopaedia articles
Lymph Node Drainage Map Dog
Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton
- thoracic cage
- ribs
- atypical ribs
- variant anatomy
- sternum
- manubrium
- sternal body
- xiphisternum
- ribs
- articulations
- thoracic cage
- muscles of the thorax
- diaphragm
- diaphragmatic apertures
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- diaphragm
- spaces of the thorax
- superior thoracic aperture
- mediastinum
- thoracic plane (mnemonic)
- inferior mediastinum
- thoracic viscera
- tracheobronchial tree
- trachea
- left main bronchus
- right main bronchus
- bronchus intermedius
- tracheobronchial branching anomalies
- trachea
- lungs
- bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy (Boyden Classification) (mnemonic)
- left lung
- left upper lobe
- lingula
- left lower lobe
- left upper lobe
- right lung
- right upper lobe
- right middle lobe
- right lower lobe
- variant anatomy
- left lung
- lung parenchyma
- pulmonary interstitium
- peribronchovascular interstitium
- interlobular septum
- peribronchovascular interstitium
- bronchiole
- terminal bronchiole
- respiratory bronchiole
- terminal bronchiole
- secondary pulmonary lobule
- pulmonary acinus
- primary pulmonary lobule
- alveoli
- primary pulmonary lobule
- pulmonary acinus
- pulmonary interstitium
- hilum
- pleura
- pleural space
- fissures
- accessory fissures
- fissures
- pleural space
- bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy (Boyden Classification) (mnemonic)
- heart
- cardiac chambers
- left atrium
- left atrial appendage
- left ventricle
- right atrium
- right ventricle
- left atrium
- heart valves
- mitral valve
- aortic valve
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- coronary arteries
- left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
- circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
- right coronary artery (RCA)
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- fetal circulation
- atrial septum
- pericardium
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- superior aortic recess
- pulmonic recesses
- pulmonary venous recesses
- aortic recesses
- pericardial space
- cardiac chambers
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- axillary tail
- Montgomery glands
- Cooper ligaments
- lymphatic drainage
- variants
- supranumerary nipple (polythelia)
- accessory breast tissue (polymastia)
- tracheobronchial tree
- blood supply of the thorax
- arteries
- thoracic aorta (development)
- ascending aorta
- aortic root
- aortic arch
- subclavian artery
- internal thoracic artery
- thyrocervical trunk
- transverse cervical artery
- costocervical trunk
- variant anatomy
- branching patterns
- subclavian artery
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
- ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
- left pulmonary artery
- thoracic aorta (development)
- veins
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- variant anatomy
- brachiocephalic veins (retro-aortic)
- azygos vein (azygos system)
- variant anatomy
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
- coronary veins
- cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
- cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- arteries
- lymphatics
- thoracic lymph node stations
- innervation of the thorax
- vagus nerve
Lymph Node Drainage Anatomy
Promoted articles (advertising)
